The healing process is divided into four broad stages which are not mutually exclusive and overlap considerably.
1. Initial vascular reaction – Active Swelling
2. Inflammatory response – Passive Congestion
3. Proliferative phase – Repair
4. Remodeling
Wound healing refers to the body’s replacement of destroyed tissue by living tissue (Walter & Israel 1987). It comprises of two essential components whose differentiation is based on resultant tissue: Regeneration and Repair.
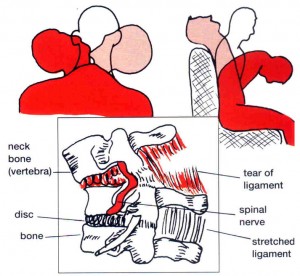
TISSUE INJURY CAUSES RESTRICTION OF MOTION DUE TO: 
- Inflammation & Swelling
- Pain
- Muscle Spasm
THE MAJOR GOALS OF CHIROPRACTIC CARE:
- Relieve Pain
- Promote Full Healing
- Restore & Maintain Full Function
- Reduce the Likelihood of Re-Injury
- Prevent Accelerated Degeneration
Chiropractic Care Should Continue Throughout the Repair Stage. It Take Longer For Tissues to Heal & Normal Function to be Restored Than it Takes for Pain Relief. Pain Relief is not the Only Goal. Chiropractic Helps:
- Restore Normal Motion, Function & Biomechanics
- Improve Alignment of New Connective Tissue
- Prevent Shortening of Scar Tissue & Chronic Stiffness
- Restore & Maintain Flexibility of Ligaments & Muscles
- Restore Normal Muscle Tone
- Promote Quicker, More Effective Healing
- Restore & Maintain Normal Sensation
- Reduce the Risk of Re-Injury and Degeneration
STAGES OF SOFT TISSUE HEALING
STAGE I: ACTIVE SWELLING

- Swelling Occurs for 12 to 72 hours
- Motion is lost and pain increases
Goals of Care: Minimize pain and swelling
Care:
- Rest & Support of Injured Area
- Ice to Block Swelling, Pain, and Spasm
STAGE II: PASSIVE CONGESTION
Fluid trapped in tissues restricts motion, causes pain, & delays healing. Begins by second to fourth day
Goals of Care for Passive Congestion:
- Remove fluid
- Pain Relief
- Begin to restore range of motion
Care:
- Chiropractic Adjustments Help
- restore motion
- block pain
- restore normal sensation
- relax tight muscles
- remove swelling
- accelerate healing
- Heat and Cold to Remove Fluid
- Controlled Motion Exercises
- Physical Therapy helps in Some Cases
- Acupuncture Can Help With Pain Control
STAGE III: REPAIR
Beginning 5 days after injury, scar tissue is made for up to 6 weeks. 
Lack of motion causes excess scar tissue in dense patterns disrupting normal function causing:
- Excess Scarring
- Chronic Stiffness
- Limited Range of Motion
- Poor Biomechanics
- Chronic Pain
- Weak Muscles & Ligaments
- Loss of Normal Sensation
- Poor Nutrition
- Increased risk of Re-Injury
- Accelerated Degeneration
If Motion is Restored & Maintained, Tissues Heal in a Much More Functional Way.
Coals of Repair Stage:
- Restore Normal Range of Motion
- Restore Sensation
- Promote Full Healing
- Relieve Pain
STAGE IV: REMODELING
Connective tissue remodels for better strength & flexibility. This often takes 3 to 14 week but may take up to 1 year with severe injury. 
Chiropractic Helps Achieve these Goals:
- Improve & Maintain Motion & Flexibility
- Restore & Maintain Function
- Reduce Chronic Pain
- Reduce Risk of Re-Injury & Degeneration
This Post was based on Dr. Malik Slosberg’s Research.